Jan 21, 03 · Calculation of probability (risk) vs odds In statistics, odds are an expression of relative probabilities, generally quoted as the odds in favor The odds (in favor) of an event or a proposition is the ratio of the probability that the event willJul 11, 16 · The term 'Odds' is commonplace, but not always clear, and often used inappropriately The odds of an event is the number of events / the number of nonevents This turns out to be equivalent to the probability of an event/the probability of a nonevent You'll often see odds written as P/(1P)Odds The odds in favor of an event is the ratio of the number of ways the outcome can occur to the number of ways the outcome cannot occur # of ways the event CAN occur # of ways the event CANNOT occur This is actually a lot easier than probability

12 7 Probability And Odds 1
Betting odds vs probability
Betting odds vs probability-Feb 23, 21 · Understanding odds conversion to the percentage and implied probability behind the odds on offer is key to assessing the potential value in a particular betting market And it is just as important when assessing the value that exists with regards to specific oddsLabs(title ="probability versus odds") 000 025 050 075 100 0 50 100 150 odds p probability versus odds Finally, this is the plot that I think you'llfind most useful because inlogistic regression yourregression equation,eg,βˆ 0 βˆ 0 ·x 1 yieldsthelogodds,andyou'reinterestedinhowthatrelatestotheprobabilityof



Binary Logistic Regression With Odds Ratios Calculated For The Download Table
Odds is a see also of probability As nouns the difference between odds and probability is that odds is the ratio of the probabilities of an event happening to that of it not happening while probability is the state of being probable;Sep 14, · Probability versus Odds A case study While the definitions of these terms can overcomplicate matters, the best way to describe them in action is to look at the coin toss challenge It provides the perfect setting for an explanation of the difference between these two statistical terms because there will only ever be one of two outcomes headsOnce again, the calculation is slightly different for minus odds versus plus odds Implied Probability = (1*(Odds)) / (1(Odds) 100) Which looks like
Jul 25, 17 · If your opponent bets the same amount but is not all in, then you can only compare those odds with your probability to improve with the next card So in above example, you still have 9 outs, but can only multiply it by 2, getting the probability of 18%Though they are often used interchangeably, the concepts of odds and probabilities are distinct from each other This video briefly explains this differenceDec 06, 17 · The key is to understand the difference between odds and probability There are 4,655,0 ways you can combine 3odd3even combinations So if you play 3odd3even combination, 33 in every 100 draws will put you in 1 to 46 million advantage rather than 1
Dec 05, 09 · Odds vs Probability Probability is a mathematical assumption of chance that can be calculated using an equation The equation measures the chances for an event to occur against the total number of chances that occurrence may produceJan 19, 16 · Probability theory is an interesting area of statistics concerned with the odds or chances of an event happening in a trial, eg getting a six when a dice is thrown or drawing an ace of hearts from a pack of cards To work out odds, we also need to have an understanding of permutations and combinationsMar 04, 12 · The wikipedia page claims that likelihood and probability are distinct concepts In nontechnical parlance, "likelihood" is usually a synonym for "probability," but in statistical usage there is a clear distinction in perspective the number that is the probability of some observed outcomes given a set of parameter values is regarded as the likelihood of the set of parameter



12 7 Probability And Odds 1



Binary Logistic Regression With Odds Ratios Calculated For The Download Table
If the probability of success is 5, ie, 5050 percent chance, then the odds of success is 1 to 1 The transformation from probability to odds is a monotonic transformation, meaning the odds increase as the probability increases or vice versa Probability ranges from 0 and 1 Odds range from 0 and positive infinityFeb 25, · An odds is the ratio of the probability of an event to its complement $$\text{odds}(X) = \frac{P(X)}{1P(X)}$$ An odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of the odds of an event in one group (say, $A$) versus the odds of an event in another group (say, $B$) $$\text{OR}(X)_{A\text{ vs }B} = \frac{\frac{P(XA)}{1P(XA)}}{\frac{P(XB)}{1P(XB)}}$$Sep 19, 14 · Probabilities are usually given as percentages ie 50% probability that a coin will land on HEADS Odds can have any value from zero to infinity and they represent a ratio of desired outcomes versus the field Odds are a ratio, and can be given in two different ways 'odds in favor' and 'odds against'



Observed Versus Model Based Left Precipitation Probabilities Right Download Scientific Diagram



Odds Of Becoming Rich Versus Implausible Events Multilotto
In this matchup, there is a big difference between the two odds, indicating a much higher probability of Duke winning the game and advancing to the next round of the NCAA TournamentNegative figures The odds state how much must be bet to win £100 profit eg american odds of 1 would win £100 on a £1 bet Implied Probability Odds correlate to probability eg a 3/1 bet is expected to win one in every 4 attempts, hence the probability is 25%The probability of having the winning plate is 1 out of 25 Odds of winning = number of chances to win number of chances to draw other numbers Odds of winning = 124 (Read as "1 to 24") Odds of not winning = number of chances to draw other numbers number of chances to win Odds of not winning = 241 (Read as "24 to 1")



How To Calculate Odds 11 Steps With Pictures Wikihow


The Odds Of Becoming A Millionaire
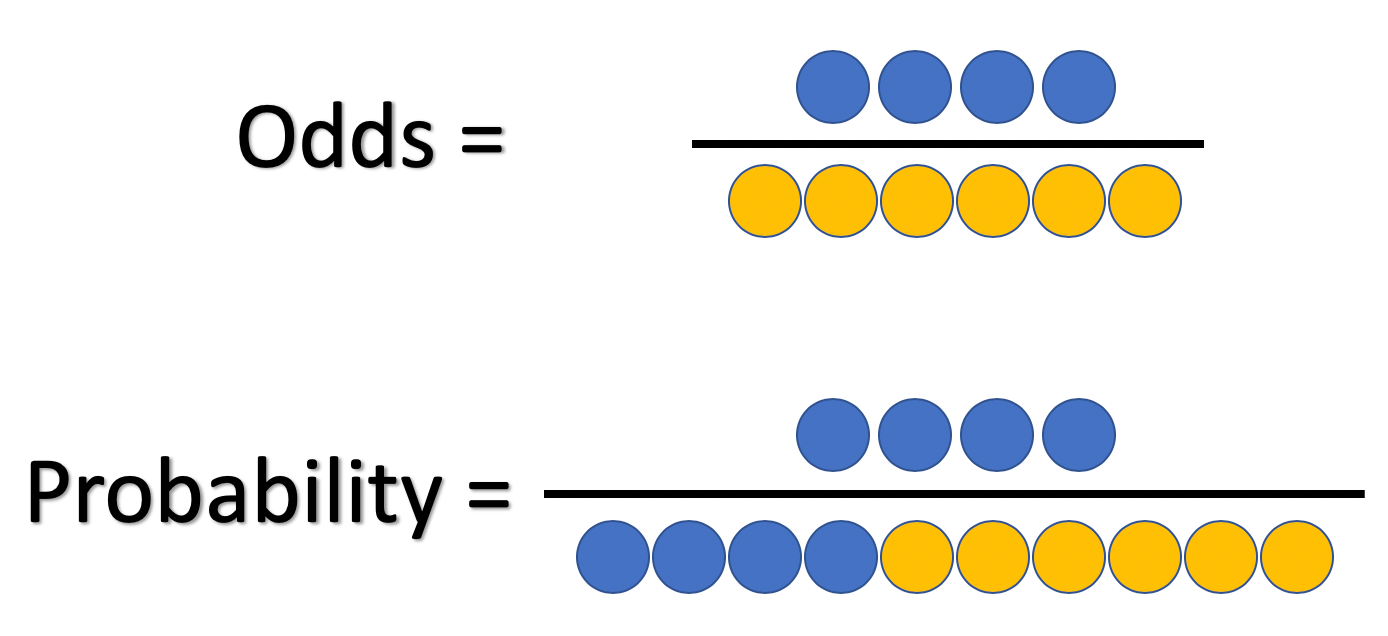
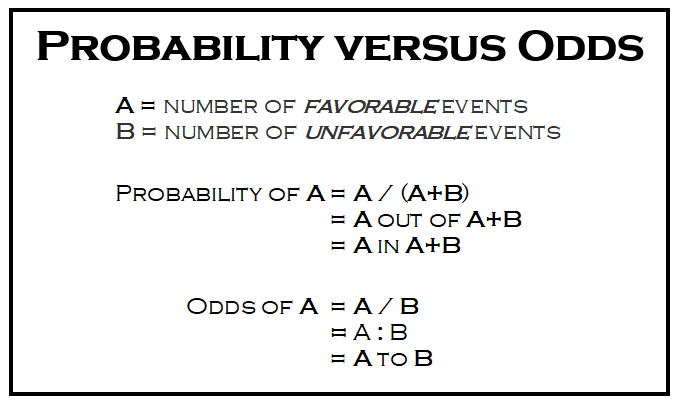
Probability vs Odds Any chance can be numerically described as either odds or probabilities In the majority of circumstances, neither is preferable to the other The majority of scientists generally refer to probabilities, not odds, but that is more a matter ofOdds, are given as (chances for success) (chances against success) or vice versa If odds are stated as an A to B chance of winning then the probability of winning is given as P W = A / (A B) while the probability of losing is given as P L = B / (A B) For example, you win a game if you pull an ace out of a full deck of 52 cardsNov 02, 13 · With that in mind, the key thing to know today is that probability and odds both describe how likely it is that something will happen—but they do it in different ways Which means that probability and odds do not mean the same thing (although we can convert from one to



Odds Introduction Arbital


Ctspedia Ctspedia Oddsterm
Probability and Order Versus Evolution BY HENRY M MORRIS, PHD SUNDAY, JULY 01, 1979 That is, the odds are at least 36,000 to one against any random assemblage of ten components into a meaningful system, which could possibly serve as a base or pattern for anythingJul 27, 11 · Odds, chances and probability are just different ways of expressing the likelihood of an event In your example of the jackpot that hits on average once per 100,000 spins, the probability of hitting the jackpot is Many people haveFeb 28, 19 · Dice Probability Introduction Before you play any dice game it is good to know the probability of any given total to be thrown First lets look at the possibilities of the total of two dice The table below shows the six possibilities for die 1 along the left column and the six possibilities for die 2 along the top column



Probability Vs Odds What S The Difference Learn It And By Z Ai Towards Data Science



Math 30 2 Probability Odds Acceptable Standards 50 79 The Student Can Express Odds For Or Odds Against As A Probability Determine The Probability Ppt Download
Probability and odds are two related concepts, but they are not mathematically equivalent Therefore, discussing probability and odds must include their difference in meaning and in scale Some think it matters not what term is used, as long as you get the gist However, it could lead to flawed decision making and incorrect estimates ofJan 05, 09 · Equal odds are 1 1 success for every 1 failure 11 Equal probabilities are 5 1 success for every 2 trials Odds can range from 0 to infinity Odds greater than 1 indicates success is more likely than failure Odds less than 1 indicates failure is more likely than success Probability can range from 0 to 1Jun 02, 09 · Odds Is Related to Probability The formal way to describe the odds is as the probability of the event divided by the probability of the nonevent So odds are the ratio of two fractions the number of events divided by the number of subjects (the probability of the event) and



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



Ppt Odds Vs Probabilities Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
Jan 26, 19 · The smaller the probability, the more similar probability and odds will be For example, the probability of winning the UK National Lottery is The odds are The larger the probability, the larger the difference with the odds High probabilities have astronomical odds A probability of 90% equates to oddsJan 19, 19 · Probability to Odds Calculator More about the Probability to Odds Calculator so that you can better understand the elements used in this calculator It is common for people to have a confusion between the concepts of odds and probability, and often times, they incorrectly use them, most typically interchanging probability by oddsFeb 19, 18 · The differences between odds and probability are discussed in the points given below The term 'odds' is used to describe that if there are any chances of the occurrence of an event or not As against, While odds are expressed in the ratio, the probability is either written in percentage form or
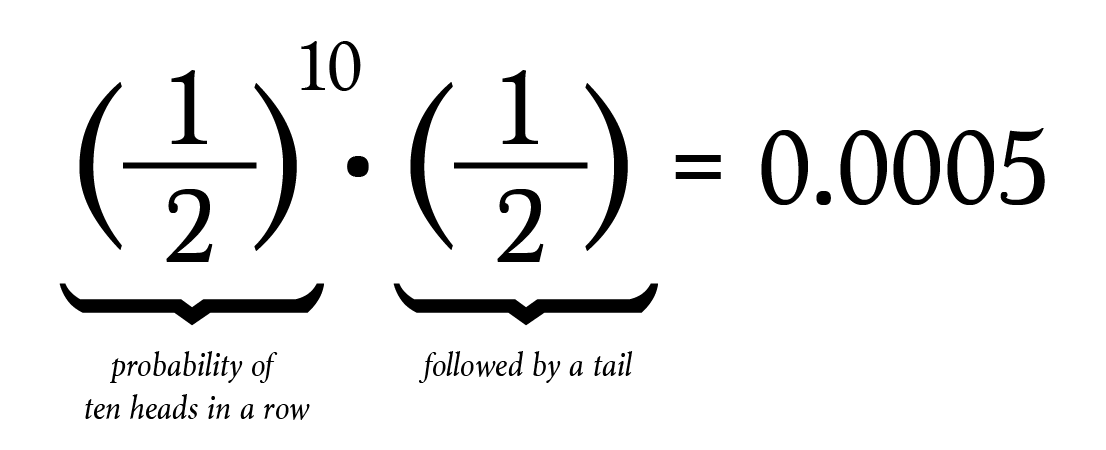


That Common Misconception About Probability By Brett Berry Math Hacks Medium



Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056
Dec 14, 14 · The Ask Dr Math forum has several entries on odds versus probability Summarizing, one way to conceptualize (nontechnically) the probability of an event is the number of ways that an event can occur divided by the total number of possible outcomes The probability of heads in a fair coin flip is 1/2 (50 percent)Of probability, chances and odds are not the same For instance, the odds in favor of A are P(A) / P(Ac) = (3/4)/(1/4) = 3/1 It is said that the odds in favor of A are 31 or that A is an event twice as likely as "not A" Therefore, the odds of A occurring are expressed in the scale of the probability of "A not occurring"Aug 12, 19 · To express odds as a probability, or the other way around, requires a calculation The natural way to interpret odds for (without calculating anything) is as the ratio of events to nonevents in the long run A simple example is that the (statistical) odds for rolling a three with a fair die (one of a pair of dice) are 1 to 5



Odds Ratio Calculation And Interpretation Statistics How To



Giant Battling Robots Probability Versus Odds
Dec 07, · American odds are sometimes called moneyline odds and are accompanied by a plus () or minus () sign, with the plus sign assigned to the lower probabilityApr 12, 19 · Probability compares the number of successes to the total number of attempts made The odds in favor of an event compares the number of successes to the number of failures In what follows, we will see what this means in greater detail First, we consider a little notationMar 23, 09 · The odds are defined as the probability that the event will occur divided by the probability that the event will not occur A probability of 0 is the same as odds of 0 Probabilities between 0 and 05 equal odds less than 10 A probability of 05 is the same as odds of 10 Think of it this way The probability of flipping a coin to heads is 50%



How To Read And Calculate Sports Odds Everything You Need To Know Betting 101


Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
Oct 24, · Odds can be expressed as a ratio of the probability an event will happen divided by the probability an event won't happen Odds in favor of A = A / (1 A), usually simplified to lowest terms, For instance, if the probability of an event occurring is 075, then the odds for it happening are 075/025 = 3/1 = 3 to 1 for, while the probability that it doesn't occur is 1 to 3 againstFeb 03, 14 · Converting between odds and probability Converting Odds to Probability Simply add the 2 components of the odds together to make a new denominator, and use the old numerator eg If the odds are 35, or 3 to 5, the probability is 3 ÷ (35) = 3/8 = 375% Converting Probability to Odds Take the probability, and divide it by its complimentHow to find probability and odds and the difference between the two We also discuss experimental probablility, theoretical probability, odds in favor, and



Odds Probability The Difference Explained With Examples
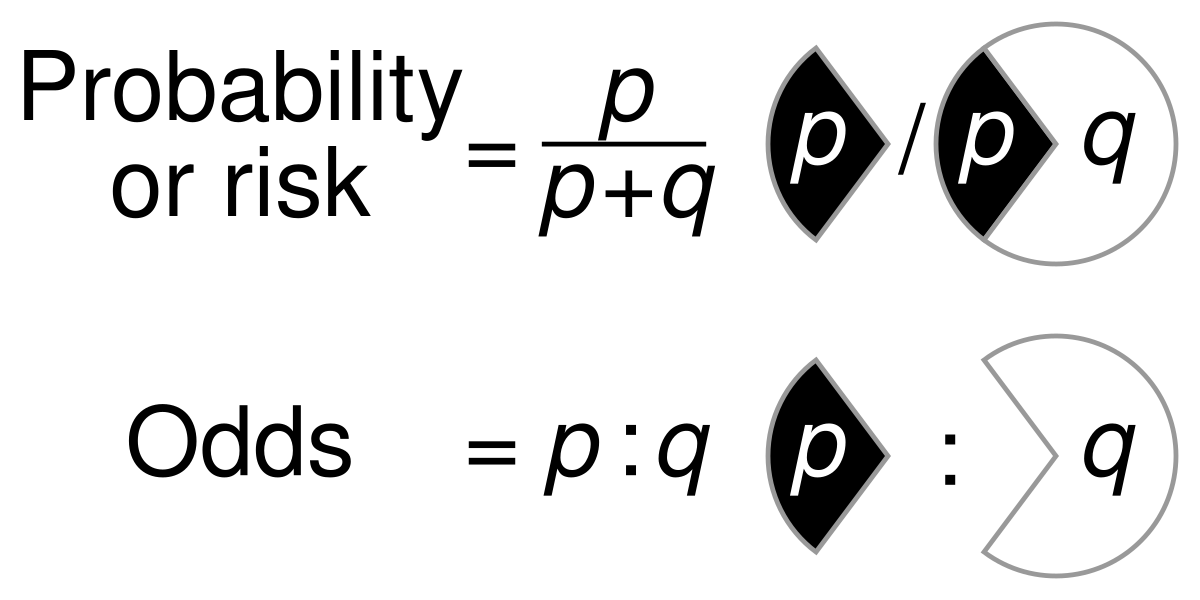


File Probability Vs Odds Svg Wikimedia Commons
Jul 31, 11 · • Probability is expressed as a number between 0 and 1, while Odds is expressed as a ratio • Probability ensures that an event will occur, but Odds



The Binomial Applied Absolute And Relative Risks Chisquare



Probability Test Review What Are Your Chances Of Passing Ppt Download



Introduction To Discrete Probability Epp Section 6 X



How To Calculate Odds 11 Steps With Pictures Wikihow



Probability Vs Odds Probability Vs Odds Explained Let Me Clarify The Difference Between Probability And Odds The Probability Of An Event Is Defined Course Hero
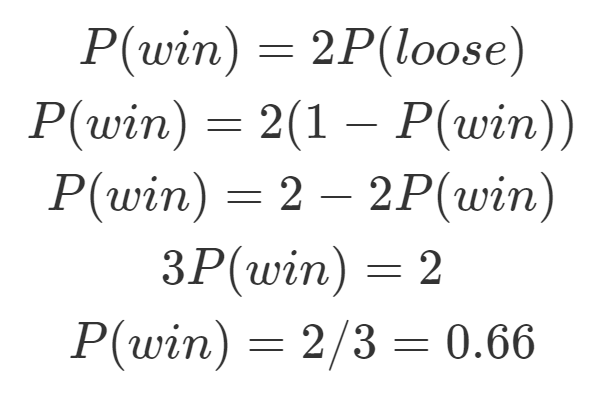


Probability Vs Odds What S The Difference Learn It And By Z Ai Towards Data Science



Statistics 12 Probability Vs Odds Stats Seandolinar Com



How To Calculate Odds 11 Steps With Pictures Wikihow



Nhanes Tutorials Module 10 Logistic Regression



Statquest Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube



Odds Ratios Of Abortion Versus No Abortion Probabilities During A Prrsv Download Scientific Diagram
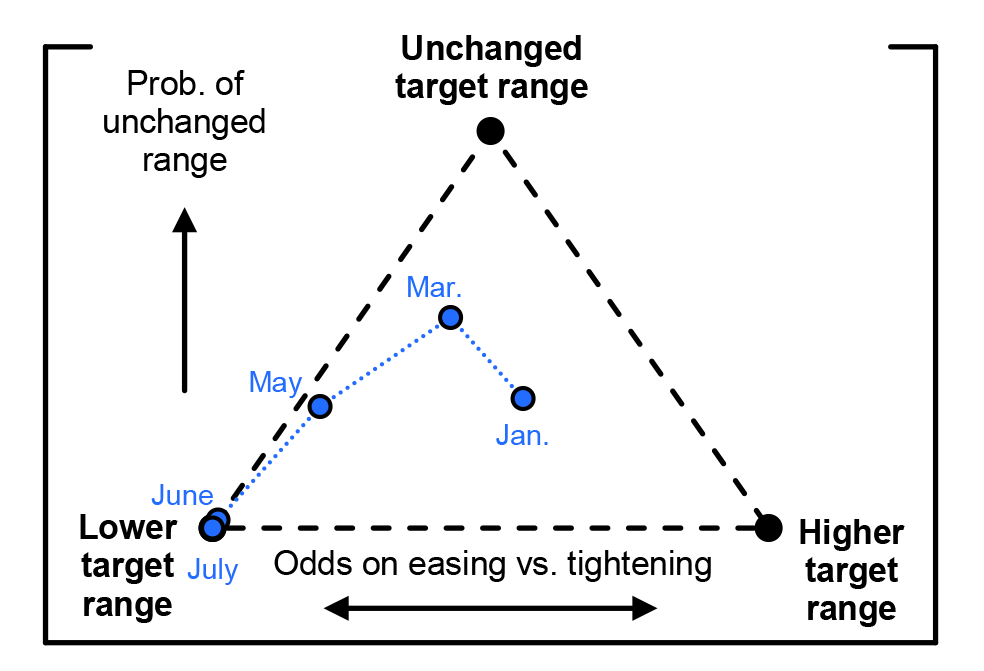


The Fed A New Way To Visualize The Evolution Of Monetary Policy Expectations


The Difference Between Probability And Odds



Odds Ratio Relative Risk


Odds Likelihood Ratios Guide To Diagnostic Tests
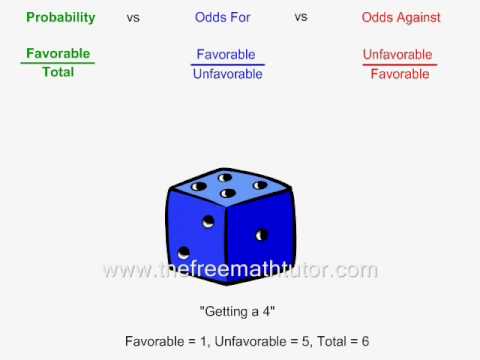


Comparing Probability Odds For And Odds Against Youtube
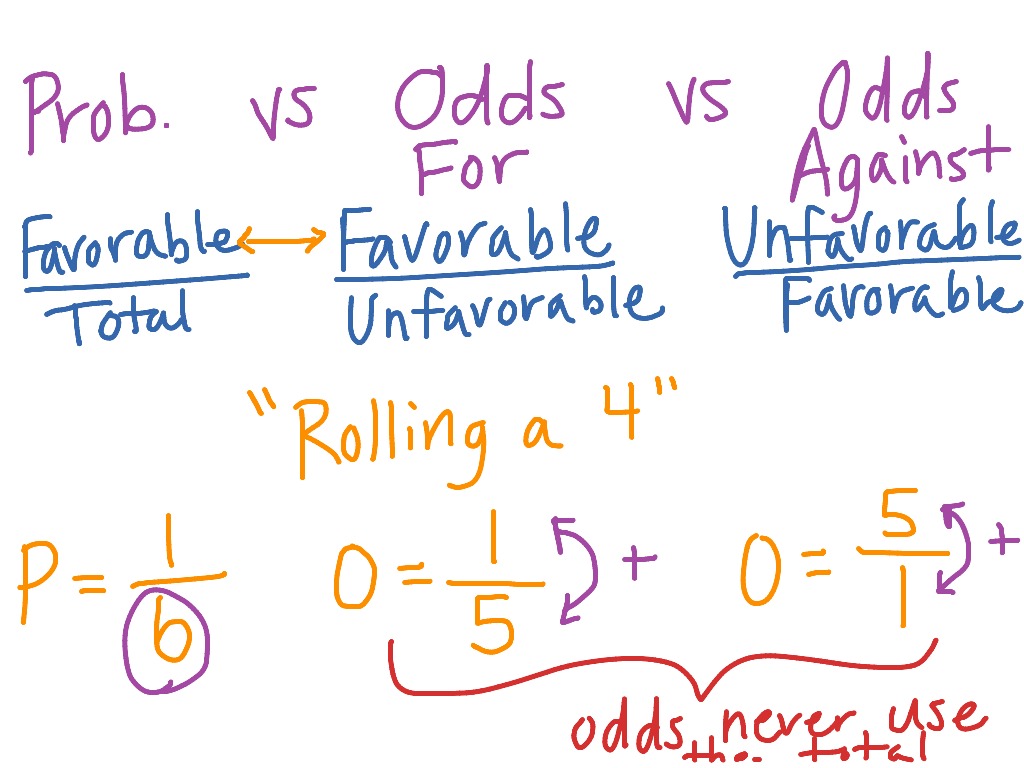


Odds Versus Probability Math Showme
/CompoundProbability2-9402bf638f6e4da9882dbdbd23dbd918.png)


Compound Probability Definition


Odds Vs Probability Vs Chance Data Science Central
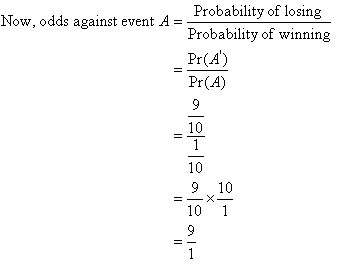


Odds



Difference Between Odds And Probability Casinosss
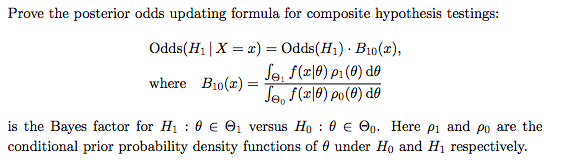


Solved Prove The Posterior Odds Updating Formula For Comp Chegg Com



Probability Vs Odds In Favour Or Against An Event Examples Youtube


Converting Between Probability And Odds Mathwoes Youtube


Odds Likelihood Ratios Guide To Diagnostic Tests



What Is The Difference Between Odds And Probability Statistics Youtube


Linear Vs Logistic Probability Models Which Is Better And When Statistical Horizons



What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal


Odds Vs Probability Vs Chance Data Science Central


Betting Odds Explained Sport Betting Guide 8sport


Odds Vs Risk Vantage Research



Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube



Probability Vs Odds In Favour Or Against An Event Examples Youtube



12 7 Probability And Odds 1


Odds Probability Calculator



Difference Between Odds And Probability With Comparison Chart Key Differences



Sportsbetting Tips Understanding Probability



Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk



Probability Vs Odds What S The Difference Learn It And By Z Ai Towards Data Science


9 2 Binary Logistic Regression R For Health Data Science
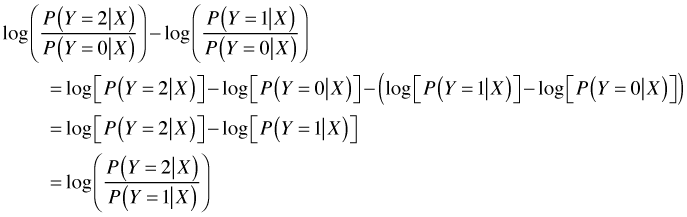


Lecture 38 Monday April 16 12
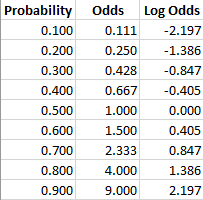


Log Odds Definition And Worked Statistics Problems
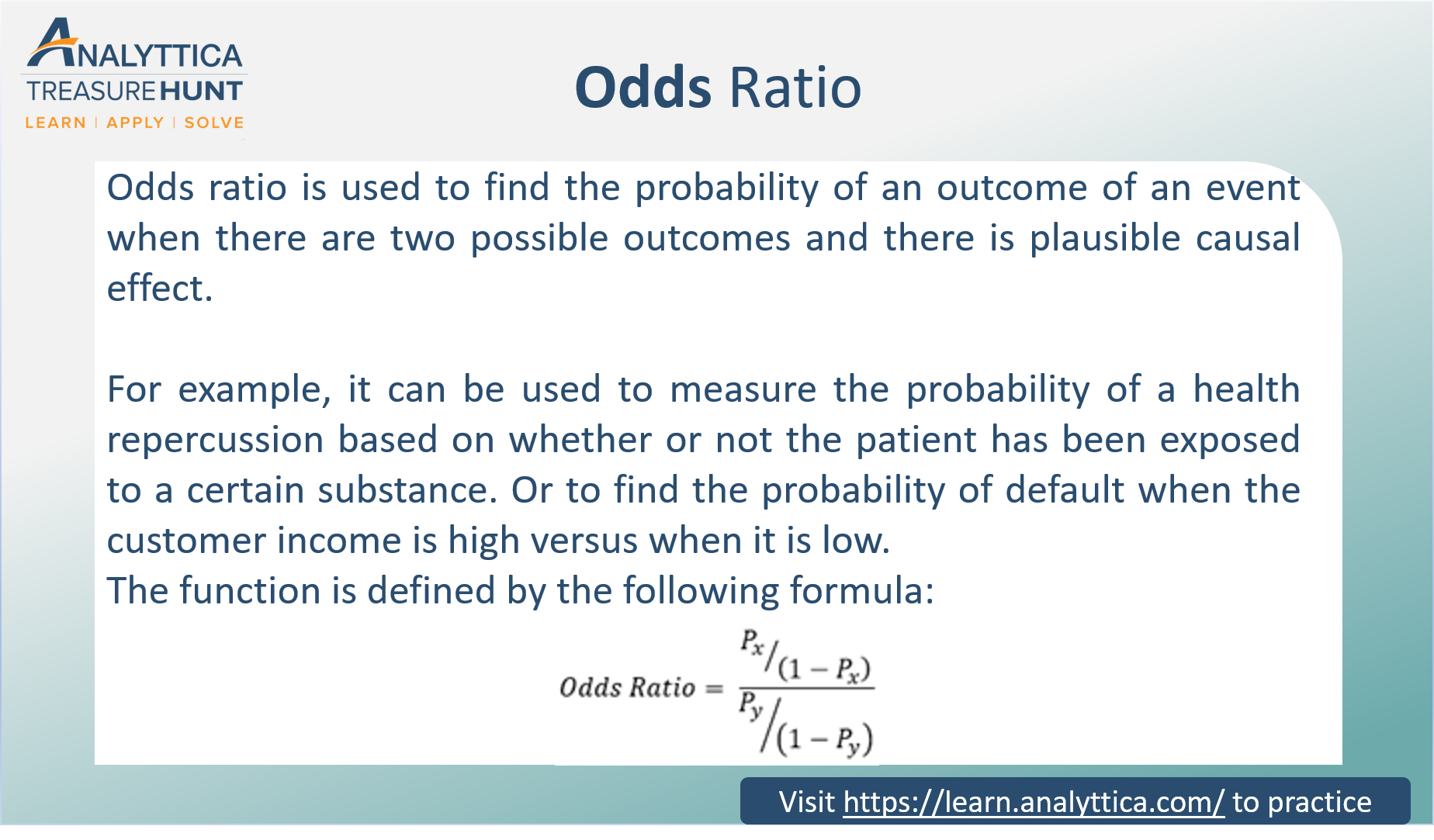


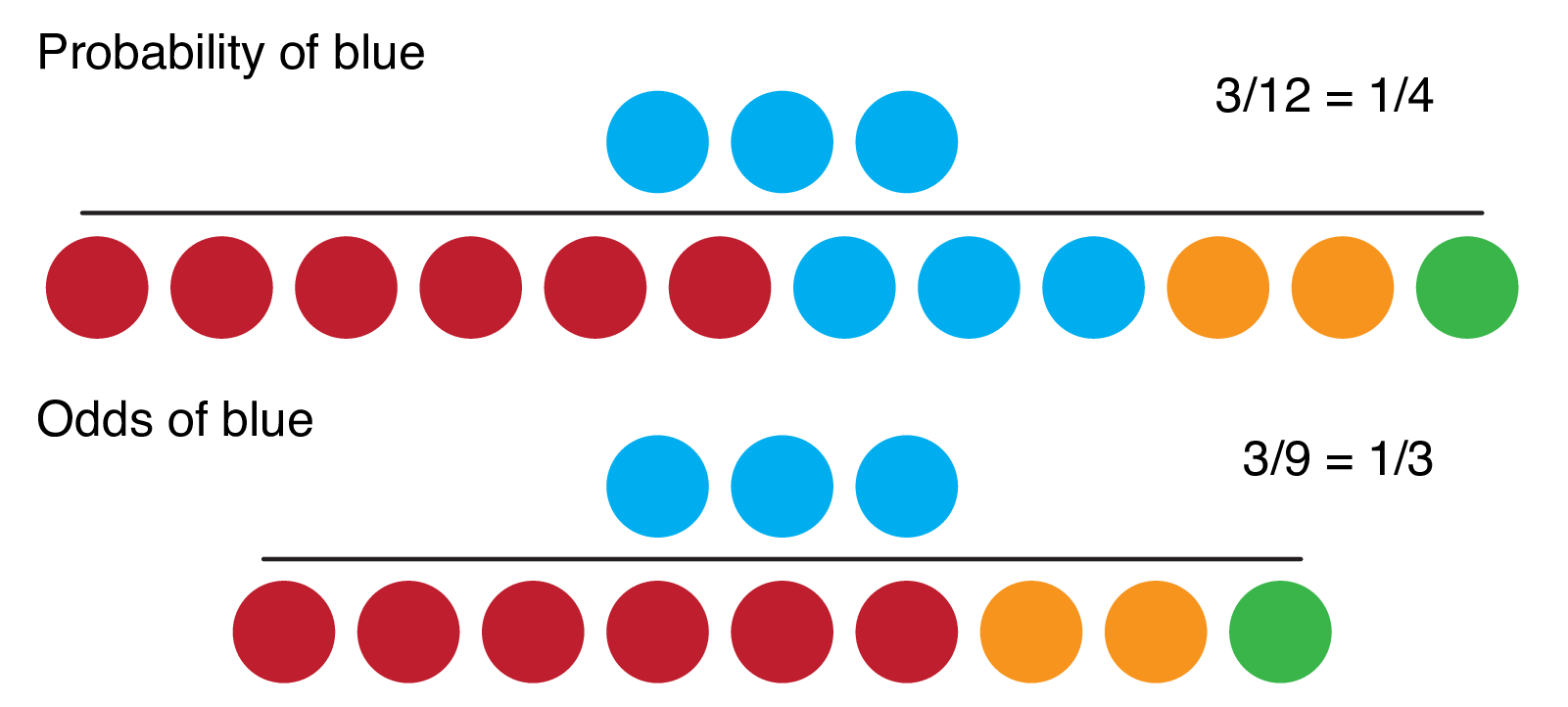
Odds Ratio The Odds Ratio Is Used To Find The By Analyttica Datalab Medium



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Probability And Odds Worksheets Teaching Resources Tpt


Odds Vs Probability Casino Spies


Are You Mixing Up Odds With Probability By Keith Mcnulty Towards Data Science



Probability Probability Vs Odds Lesson Video By J Thompson Tpt
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_The_Math_Behind_Betting_Odds_and_Gambling_Nov_2020-01-735accb453c8424b9e063c2c14e4edf4.jpg)


The Math Behind Betting Odds Gambling



Implied Probability Betting Math Made Simple 21 Update


Probability Vs Odds What S The Difference Learn It And By Z Ai Towards Data Science



How Sports Betting Odds Work How To Read Odds Explanation Video



Simple Probability Definition Probability The Chance Some Event



Probability Vs Odds What S The Deal With State Lottery Odds Table



Binary Logistic Regression With Odds Ratios Calculated For The Download Table


Probability Probability Vs Odds Lesson Math Statistics Showme



Odds Probability And The Lottery Lotterycodex



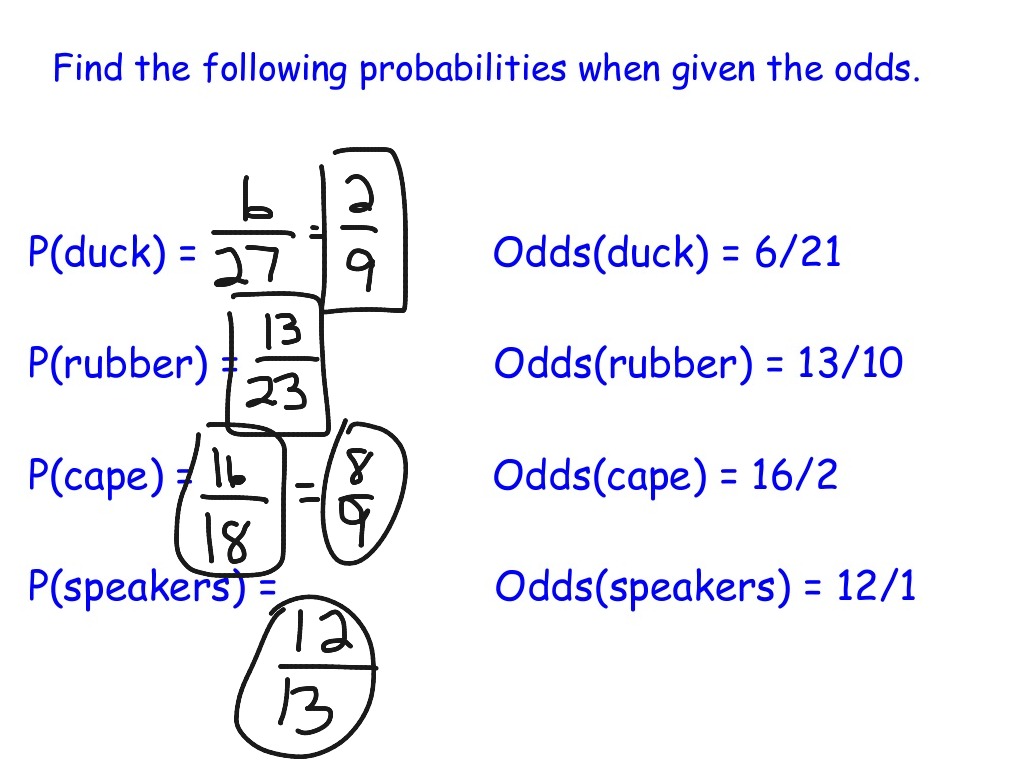
Solved 9 6 Odds To Probabilities 1 If The Odds Of An Chegg Com



The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor



Probability Vs Odds Youtube



Converting Between Probability And Odds Mathwoes Youtube


What And Why Of Log Odds What Are Log Odds And Why Are They By Piyush Agarwal Towards Data Science



Piq Betting Odds For Trump In Vs 16 Very Similar Pattern As 16 Developing Though This Time Trump Is Starting From A Much Higher Probability Of Winning Jpm


What Are The Odds Stats With Cats Blog
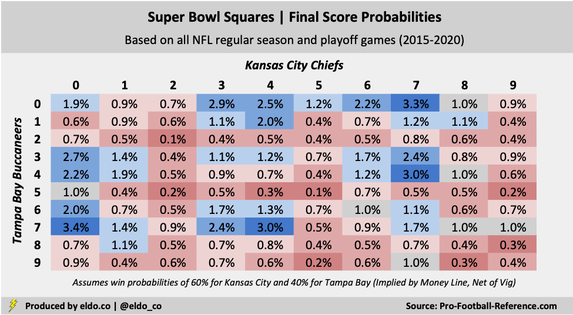


Super Bowl Squares Odds 21 Best Worst Numbers Eldorado



Probability And Odds Youtube


Faq How Do I Interpret Odds Ratios In Logistic Regression



What Are The Odds The Annals Of Thoracic Surgery


What Are The Odds Stats With Cats Blog



Converting Probability To Odds Example Youtube



Part 3 Module 3 Probability Suppose We Create



Probability Vs Odds Math Probability Showme



Are The Odds Ever In Your Favor Car Crashes Versus Other Fatalities News Cars Com



Probability Vs Odds What S The Difference Learn It And By Z Ai Towards Data Science



Pregame Probability Real Odds Betpractice Tutorials



Probability



Biostatistics Weeks 10 11 Flashcards Quizlet



Lecture 5 Basic Probability David R Merrell 90



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



What And Why Of Log Odds What Are Log Odds And Why Are They By Piyush Agarwal Towards Data Science



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿